Editing a text file
A text file contains all defined text modules and lists them in a table. These outsourced texts are used, for example, for editing buttons, information texts in the editor, etc. and can therefore be managed globally.
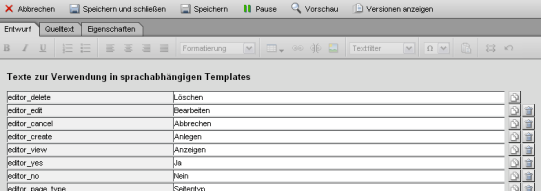
Editing a text file
Operation
You can create, edit and delete text modules in the 'Draft' tab. Via the 'Metadata' tab, you can access the metadata for the text file, which is only relevant because of the title (see text directory). The 'Properties' tab allows you to define various file properties (online status, etc.), which will not be discussed further here.
'Copy':
By clicking on the copy symbol'Delete':
You can remove a text entry from the text file by clicking on the recycle bin symbolIf this text module is still used within the project, only the text module name (e.g. editor_delete) and no longer the (language) text defined for it is displayed in its place.


