Project configuration - Editing the variable file
A variable file contains all defined variables and lists them in a table. These variables are used in the BASE for the project configuration in order to output a general title, banner, logo, etc., uniformly on all pages.
In the BASE, the variables are primarily used for the project settings (configuration) and can be accessed via the Weblication® panel or via the backend under the administration of the global project.
Operation
You can edit the variables in the 'Draft' tab. By default, an edit mask is supplied with the BASE, which can also be customized.
Via the 'Metadata' tab, you can access the metadata for the variable file, which is only relevant because of the title (see variable directory). The 'Properties' tab allows you to define various file properties (online status, etc.), which will not be discussed further here.
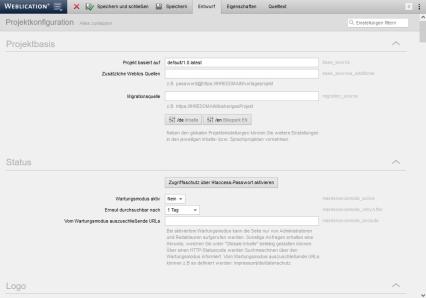
The editing and definition of variables is explained below using the"General project configuration" of the BASE as an example.
The variables are already predefined in the BASE and displayed via a corresponding editing mask in the 'Draft' tab. For the sake of clarity, the variables are grouped and listed under the corresponding heading (e.g. master data). A description text (e.g. page title prefix), the corresponding form field (e.g. input field, selection box, file selection, etc.) and the key of the respective variable (e.g. title_prefix) are displayed for each variable.
The key of the variable is used to address it in the corresponding templates (see: Framework function "wVariables::getValue"). You can define the value of the corresponding variable via the respective form field.
For the developer/programmer:
Make sure that no variables occur more than once within the variable file. The variable that occurs first is always used. If a variable is used within a project that is not defined, only the variable name (e.g. title_prefix2) and not the definition defined for it is implemented in its place. In addition, this variable that does not yet exist in this variable file is added at the end so that it can be defined precisely.


